How Concussions are Underdiagnosed Amid Head Injury Awareness by Dr John Manzella
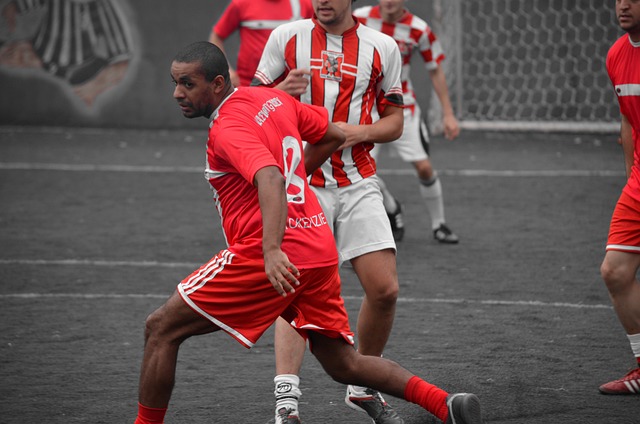
Concussions are generally caused by a blow to the head and can cause brain swelling, which can lead to other complications, including second-impact syndrome states Dr John Manzella. While concussions are more common than you might think—an estimated 1.6 million people in the United States alone get them each year—many people don't realize they've suffered one until days or weeks after they've happened. This is because symptoms of a concussion (which include headaches and dizziness) don't always appear right away. It's important to see a doctor if you think you or someone else has had a concussion so it can be diagnosed properly and treated accordingly.
Medical experts are concerned
that concussions are still underdiagnosed even amid increased awareness and concern.
“Concussions are a public health issue,” says Chris Nowinski, co-founder and CEO of the Concussion Legacy Foundation. “If these injuries were happening in other parts of our lives, there would be a lot more awareness and concern about it.”
Nowinski points to the NFL's concussion protocol as an example of how progress can be made when organizations take concussions seriously: “The way they're handling concussions now is a marked improvement over where they were 10 years ago. When people look back on this era in football, they will think 'that was ancient history,' but at the time no one knew what they know now."
Undiagnosed concussions
increase the risk of complications, including the very serious second-impact
syndrome.
Second-impact syndrome can occur when a person is hit again before her brain has recovered from the first.
Unlike other concussions, the symptoms of second-impact syndrome are rapid and severe. Symptoms include:
● Coma or unconsciousness for more than 24 hours
● Increased intracranial pressure (pressure in the skull) that worsens over time
Doctors have new guidelines
for concussion management in children and adults.
The new guidelines are the first to specify that the combination of concussion symptoms, such as headaches and dizziness, warrants a trip to the doctor's office.
The guidelines also recommend that children and teenagers diagnosed with concussions should avoid vigorous exercise and sports until their symptoms clear up, as well as some schoolwork until they've fully recovered.
For adults, doctors are urged not to return patients who have had concussions back into stressful situations too soon.
Concussions are serious head
injuries and should be evaluated by a health care professional as soon as
possible after a blow to the head.
Concussions are serious head injuries that should be evaluated by a health care professional as soon as possible after a blow to the head. Concussions can occur in any sport or recreational activity, including contact and noncontact sports, such as football and hockey; falls; and car accidents.
Concussions can cause symptoms such as:
● Dizziness or feeling lightheaded
● Headache or pressure in your head
● Nausea or vomiting
Conclusion
Concussions are serious head injuries, and they have the potential to cause lifelong problems. Because they can be difficult to diagnose and treat, it’s crucial that you get medical attention as soon as possible after any blow to your head. If you or a loved one suffers from concussion symptoms such as nausea, vomiting or dizziness, seek medical attention right away.


Comments
Post a Comment